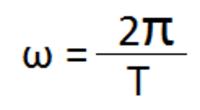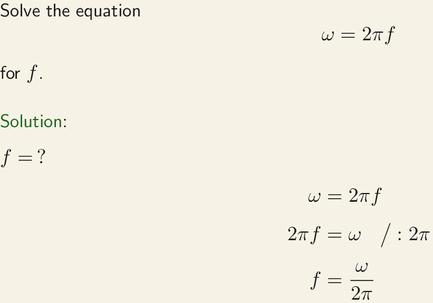Find the vector sum of n coplanar forces, each of magnitude F, when each force is making an angle of 2/n with the preceding one.
![A periodic function f(x) of period 2π is defined as f(x)= {(-1, for [-π, 0] and 1, for [0, π] - YouTube A periodic function f(x) of period 2π is defined as f(x)= {(-1, for [-π, 0] and 1, for [0, π] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/5K-q9bjAbL0/hqdefault.jpg)
A periodic function f(x) of period 2π is defined as f(x)= {(-1, for [-π, 0] and 1, for [0, π] - YouTube
How does the term sin (2*pi*f*t) come from? I know that sin and cosine take radians as arguments which will be (pi/2) * (no. of degrees) but why do we mulitply f*t?
![Consider the function f(x)=(x+2)/cos(x) with the domain [0,2pi]. Where is f(x) continuous on [0,2pi]? Express your answer in interval notation. | Homework.Study.com Consider the function f(x)=(x+2)/cos(x) with the domain [0,2pi]. Where is f(x) continuous on [0,2pi]? Express your answer in interval notation. | Homework.Study.com](https://homework.study.com/cimages/multimages/16/screen_shot_2018-08-09_at_5.17.40_pm5485221551351391721.png)
Consider the function f(x)=(x+2)/cos(x) with the domain [0,2pi]. Where is f(x) continuous on [0,2pi]? Express your answer in interval notation. | Homework.Study.com

Continuum extrapolation of the form factors f 1 (v · p π ) + f 2 (v · p... | Download Scientific Diagram